10 June 2021, 13:06
Tagline
10 June 2021, 13:06
Tagline
Trade can be complex and complicated, reflecting the nature of supply chains stretching around the world.
As identified in the FATF’s 2018 Professional Money Laundering report, Trade-based Money Laundering is one the methods most preferred by money launderers. It is often combined with the use of front companies, front men, and other ML techniques.
Trade-based money laundering is highly adaptive and can exploit any sector or commodity. These are exploited by Professional Money-Launderers and Terrorist Financing networks, to facilitate myriad types of financial flows, including the laundering of proceeds of crime, such as from drug trafficking; the financing of terrorism; and the evasion of sanctions.
TBML can involve the import and export of goods and the exploitation of a variety of cross-border trade finance instruments.
The traditional techniques were described in the initial 2006 FATF report and include:
These continue to be used for ML purposes as they are highly flexible and adaptable, despite changes in global trading patterns and the growth of new markets. These techniques are particularly effective when there is a complicit relationship between the importer and exporter, who are actively misrepresenting an aspect of the trade or the associated invoice settlement process. Therefore, authorities can have a greater impact if they can disrupt these complicit actors, whether through criminal prosecution or another form of disruption – e.g. removing their authority to trade
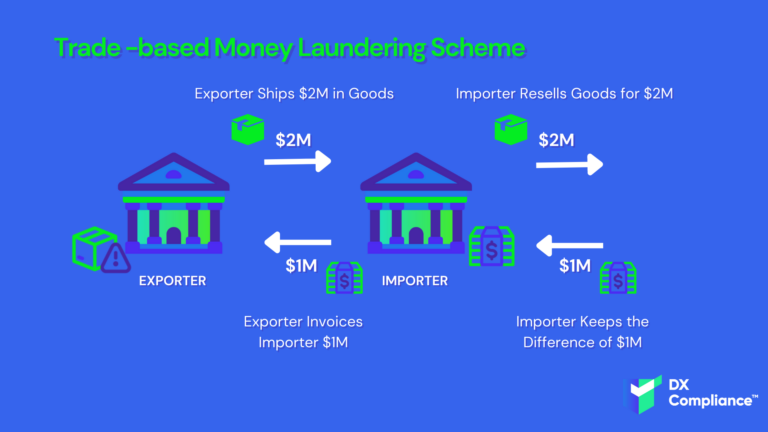
Recently FATF in co-operation with the Egmont Group, the FATF has released a report about Risk Indicators related to TBML. The indicators are derived from a sampling of the data received by the FATF and the Egmont Group of FIUs in the course of the TBML project. These updated Risk Indicators from March 2021 can help public and private entities identify suspicious activity associated with it.
3 very common methods relate directly to invoicing these are called over-invoicing, under-invoicing, multiple-invoicing, and relate directly to charging a different amount than is due for the goods/services in question.
Another method, related directly to this, is often to misrepresent the quality of the goods in question to leave a gap between value or cost and the amount paid.
Recently in the media were also 4 Covid-19 not related common methods:
The right transactions monitoring system in place that uses all your data points makes it much easier to find suspicious cases.
Private Sector: http://www.fatf-gafi.org/media/fatf/documents/Handout-Trade-Based-Money-Laundering-Private-Sector.pdf
Public Sector: http://www.fatf-gafi.org/media/fatf/documents/Handout-Trade-Based-Money-Laundering-Public-Sector.pdf

08.08.2022
An overview of recent AML developments in the UAE.
Get access
15.10.2021
The introduction of 6AMLD regulations aims to reduce financial crimes.
Get access
27.07.2021 AML Compliance
Uncovering the PEP and Sanctions Lists and Global Regulation
Get access