29 November 2022, 11:07
Tagline
29 November 2022, 11:07
Tagline
There is no single global definition for Decentralized Finance. DeFi can be described as a movement that has evolved from a decade of experimentation with cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology to overcome traditional centralized financial intermediaries.
The Bank of England’s Financial Policy Committee defines DeFi as…
… a collective term for a set of applications that seek to provide a range of financial services, including loans and exchanges, with the aim of reducing reliance on centralized financial intermediaries. These alternative financial applications are built on distributed ledger technology. Unlike traditional financial services firms that undertake these activities, DeFi applications are, at present, worldwide largely unregulated.
But what does it mean? Decentralized finance eliminates the need for middlemen by enabling financial transactions to be conducted in a direct way, so to speak, via new technologies. Through peer-to-peer financial networks, DeFi leverages security protocols, connectivity, software and hardware advances.
Anywhere there is an Internet connection, financial actions (lending, trading, and borrowing money) can be performed through software . A distributed database is accessible across different locations because it collects and aggregates data from all users and uses a consensus mechanism to verify it.
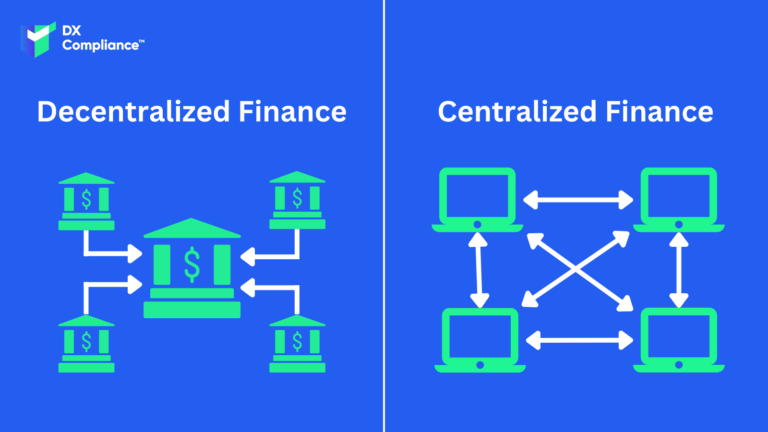
Traditionally in centralized banking, banks are responsible for the (secure) execution of financial transactions. With DeFi people have money in a kind of digital wallet and can transfer money in seconds. DeFi thus eliminates the fees that banks and other financial companies charge for using their services.
Decentralized finance eliminates the need for a centralized financial model by enabling anyone, anywhere to use financial services. Regardless of who they are or where they are.
The FATF has produced standards for virtual assets (VAs) and virtual asset service providers (VASPs). This report comes three years after the FATF extended its anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing (AML/CFT) measures to VAs and VASPs to prevent the criminal and terrorist misuse of VAs.
Regarding financial crime compliance, the FATF noted that…
… recent outreach with industry suggests that ‘decentralized’ currently can be a marketing term rather than a technical description, and that even in so-called decentralized arrangements, often there continues to be persons and centralized aspects that may be subject to AML/CFT obligations.
With the centralized financial system, there are risks related to money laundering and other financial crimes. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) highlights that “DeFi is increasingly being used to launder money.”
In addition, the US government notes, for example, that DeFi applications convert the illicit proceeds of ransomware-related payments.
DeFi’s focus on decentralized financial transactions tests a central feature of AML policy and regulatory architecture, that generally relies on financial institution intermediaries for customer due diligence including know your customer (KYC), record keeping, and reporting like filing suspicious activity reports (SARs).
Policymakers continue to recognize that heightened AML compliance obligations do not apply to software, but not all activities self-branded as “DeFi” may benefit from this exemption. This is why AML transactions Monitoring is a crucial part in a permissionless decentralized Ecosystem. Other features of cryptoassets that apply equally to DeFi transactions may improve
AML compliance.
The public design of blockchains with immutable public ledgers are features that do not exist with other financial transactions, thereby providing compliance professionals, regulators, and law enforcement with new tools for blockchain and transaction analytics is important.
The above-mentioned FAFT regulations for virtual asset service providers need to be adopted. But this is a challenge for many. Virtual asset service providers need to familiarize themselves with the financial regulations that now apply to their sector.
To overcome this hurdle, it is helpful to enlist outside help. They can provide software to comply with regulations and detect suspicious transactions.
Monitoring transactions is an essential part of identifying transactions that are potentially suspicious. As a result, regulated entities must continuously monitor their customers’ transactions.
For Virtual Asset Service Providers, where large volumes of transactions occur on a regular basis, automated AML transaction monitoring systems are the only realistic method of monitoring transactions. However, even when automated systems are deployed, institutions must understand their operating rules, regularly review their integrity, and ensure they cover identified ML/TF risks.
In addition to specific transaction monitoring, ongoing monitoring goes even further. Monitoring also includes identifying changes in the customer profile (e.g., change in information, use of products) and updates that may require the application of new or additional CDD measures.
DX Compliance helps Decentralized Finance Companies and Virtual Asset Service Providers to comply with AML and monitor their risk and detect the threat of money laundering to ensure compliance and reduce the risk of being fined.
DX Compliance offers two products to support our Clients in Europe, the UAE and beyond. A world class real-time AI Transactions Monitoring system and an instant AML Check Platform called CheckAML.
Curious? Please contact our experts!

08.08.2022
An overview of recent AML developments in the UAE.
Get access
15.10.2021
The introduction of 6AMLD regulations aims to reduce financial crimes.
Get access
27.07.2021 AML Compliance
Uncovering the PEP and Sanctions Lists and Global Regulation
Get access